About me
Team
VISUS, University of Stuttgart ——– Institute of Visual Computing, Graz
Current research areas
Real-time graphics
This research focuses on scalable graphics algorithms for rendering large and complex scenes at real-time frame rates. We investigate novel approaches to techniques such as level of detail, image-based rendering, potentially visible sets, frame extrapolation and geometry compression. We are particularly interested in rendering methods suitable for streaming rendering and virtual reality displays.Situated visualizations
Situted visualization uses augmented reality displays to present information to a human user that is dynamically derived from the user's physical environment. It provides guidance, instructions and context in everyday situations. We investigate when, where and how to visualize such information, and what information to visualize.Photorealistic augmented reality
Ideally, virtual objects displayed in augmented reality would be indistinguishable from real objects. This grand challenge requires capturing the entire image formation process in reality and simulating the virtual counterpart. It encompasses reality capture, light transport, camera simulation and much more.  HandLight |  Neural Bokeh |  Learning lightprobes |
Image-based modeling and rendering
Capturing the geometry and appearance of the real world and novel view sythesis from images is a key technique for compelling extended reality techniques, such as telepresence or mediated reality. In this work, we investigate emerging scene representations, such as light fields and radiance fields.  Sorted Opacity Fields |  AAA Gaussians |  VR Photo Inpainting |
 Good Keyframes to Inpaint |  InpaintFusion: RGB-D Inpainting |  MR Light Fields |
3D reconstruction and authoring
Augmented reality applications require new types of multimedia content to deliver convincing instructions and guidance. This content is generated using techniques in the area of semantic and parameterized reconstruction combined with procedural and computer-assisted 3D authoring.Localization and tracking
Wide-area localization and tracking is key enabling technology for augmented reality. Our research investigates scalable scene descriptors, sensor fusion, and multimodal localization techniques.  Change-Resilient Localization |  Bag of Wor(l)d Anchors | 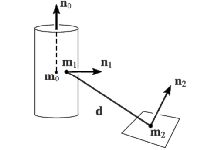 Compact World Anchors |
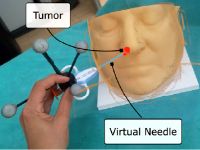 HoloLens stereo tracking | 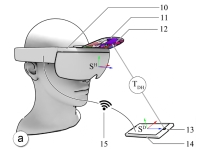 TrackCap |  VR Upper Body Pose |
Immersive displays
Conventional XR displays generate only certain types of depth cues and fall short of a hypothetical ultimate display. Our research on immersive display technology improves some of the limitations of existing XR display technology using light field approximation and focal cue synthesis.  Gaze-Contingent Layered Optical See Through | 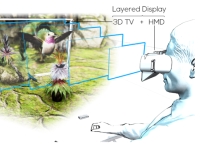 Off-Axis Layered See-Through Head Mounted Display |  Video See Through Display with Focal Cues |